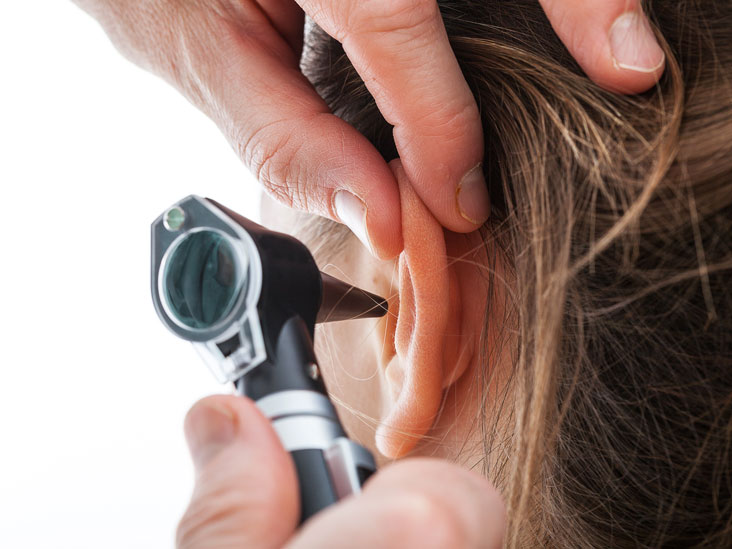
Hearing loss can be divided into various types under many categories. It is crucial to screen ears to determine what kind of hearing loss is there. One should always go for professional audiology services, like dépistage auditif Audiologie Centre-Ouest, to avoid misdiagnosis.
You can divide them based on where the problem occurs, based on intensity, and the nature of the loss.
Based on Where the Loss Occurs
Based on where the hearing loss occurs, hearing problems can be divided into three basic types:
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss usually occurs due to some damage or abnormalities associated with nerves, especially the auditory nerve. Such losses may also occur due to damages related to the inner ear.
- Conductive Hearing Loss
These hearing losses refer to losses that occur due to many sorts of damages to the middle of the outer ear. They are less severe in nature and can be treated very easily with medications. In some cases, surgery may be necessary. However, conductive auditory surgeries are very simple in nature.
- Mixed Hearing Loss
In this case, the loss can be caused by both conductive and sensorineural factors, i.e., the inner ear, middle ear, and auditory nerve can all be damaged in such cases.
Based on Intensity
Based on intensity, hearing loss can be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. Here is a brief explanation of each type of intensity.
- Mild Hearing Loss
In such cases, the individual is able to hear hard sounds but has difficulty hearing soft sounds.
- Moderate Hearing Loss
In such cases, the individual hears nothing when people around them are speaking in their normal tone and volume.
- Severe Hearing Loss
In such cases, the individual is incapable of hearing normal soft sounds when people around them are speaking in their natural tone and volume and can only listen to them when they speak loudly.
- Profound Hearing Loss
In such cases, the individual is entirely incapable of hearing normal sounds and can listen to only really loud sounds.
- Extra-Profound Hearing Loss
In such cases, the individual cannot hear whether the sounds are loud or not.
Other Types
Other types of hearing loss include unilateral, bilateral, pre-lingual, post-lingual, symmetrical, asymmetrical, congenital, fluctuating, progressive, or hearing loss.
Conclusion
Hearing problems can result from damage to various organs, both in the ears and inside. Brain injuries are highly related to hearing loss. Commonly, hearing loss occurs due to damage to the ears’ internal parts, such as the auditory nerve, eardrum, pinna, ear canal, or ossicles. Proper screening is vital to avoid misdiagnosis of hearing loss.