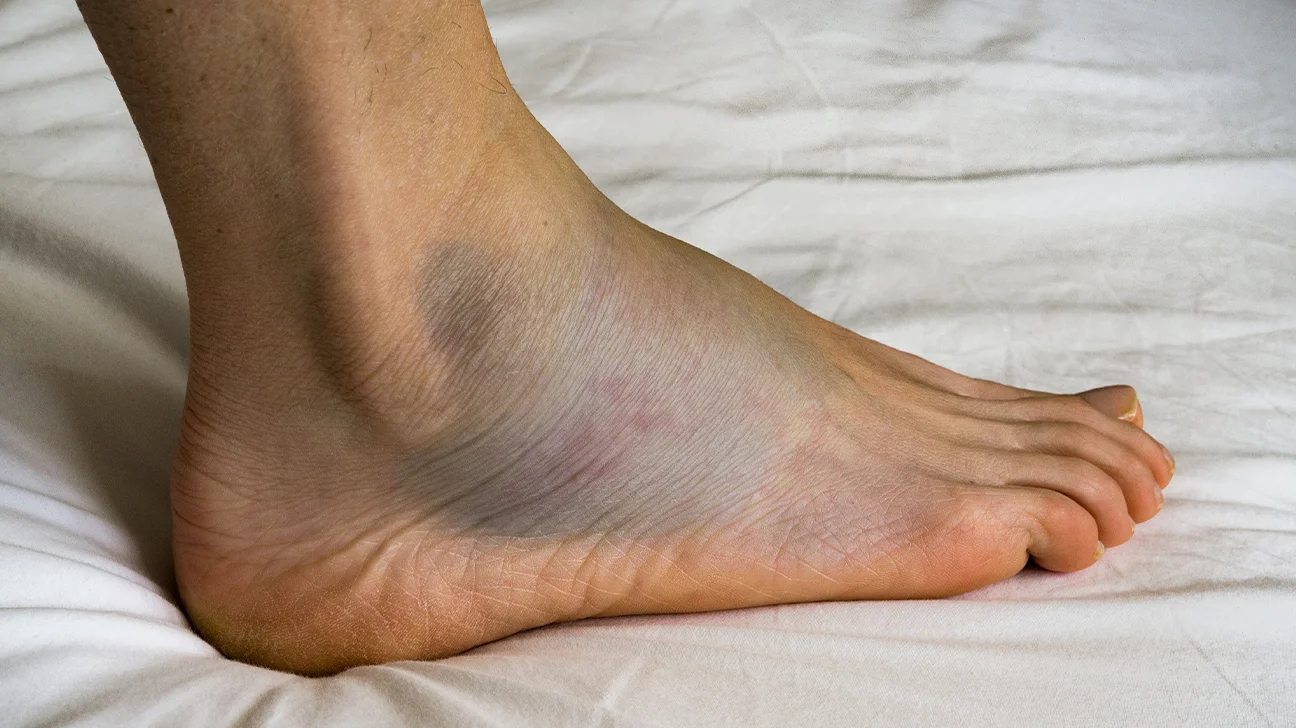
Peripheral edema, also referred as leg swelling, is a chronic illness that can affect individuals of any age. In this illness, extra fluid accumulates in the tissues of the lower extremities, causing discomfort and visible puffiness. In a busy city like Houston leg swelling can significantly affect everyday activities where a hustle culture is typical.
While it is often not an alarming condition, understanding its origin, identifying the symptoms, and being aware of how to manage it can help improve general health and well-being. In this article, we discuss the various aspects of leg swelling, from its origin to effective cure and preventative measures.
Why Do Legs Swell?
- Gravity and Circulation: Gravity causes fluid pooling; poor circulation hinders fluid return. Both lead to leg swelling (edema) due to increased pressure.
- Heart Conditions: Owing to impaired cardiac activity, conditions such as congestive heart failure can cause fluid accumulation in the legs.
- Kidney Problems and Leg edema are related because decreased kidney function can affect the body’s ability to regulate fluids.
- Venous insufficiency: When veins do not function properly, blood flow back to the heart is hampered, causing fluid retention in the legs.
- Injury and inflammation: Inflammation and injury can result in localized pain and edema.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Pitting Edema: When a swollen area is pressed, an indentation remains, which is a common symptom of pitting edema.
- Skin alterations included redness, stiffness, or shine on the skin around the swelling area.
- Pain and Discomfort: Leg swelling is often accompanied by pain, discomfort, and mobility problems.
Management and Treatment
- Lifestyle Modifications: The ailment can be treated with lifestyle changes such as elevating the leg, exercising, and consuming less salt.
- Compression therapy: The use of compression stockings or clothing aids in reducing swelling and promoting blood flow.
- Diuretics and other drugs may be recommended to treat the build-up of excess fluid.
- Management of Underlying disorders: Any underlying medical disorder that causes peripheral edema should be treated.
- Home remedies: Disseminating natural care and self-care methods that can ease discomfort and encourage healthy blood flow.
Prevention
- Regular exercise helps to avoid leg edema and maintain healthy circulation.
- Healthy Eating: A balanced, low-sodium diet helps avoid fluid retention.
- Drinking sufficient water can help maintain the body’s fluid equilibrium.
- Avoiding Extended Sitting or Standing: Extended sitting or standing may cause fluid accumulation and should be avoided
- Regular Checkups: It is important to consider regular medical checkups to maintain general health and identify any potential problems as soon as they arise.